In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, selecting the optimal software development models for your project has become a critical decision that can significantly influence the success and efficiency of your endeavor. With a plethora of methodologies available, ranging from the traditional Waterfall model to the agile approaches like Scrum and Kanban, making the right choice requires careful consideration of various factors specific to your project’s nature, scope, and requirements.
In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of different software development models, weighing their pros and cons, and providing insights to help you navigate the maze of options and choose the best-fit model that aligns with your project goals and team dynamics. Whether you’re embarking on a large-scale enterprise solution or a nimble startup application, understanding the nuances of each development model will empower you to make an informed decision that sets the stage for a successful software development journey.
 The Waterfall model is one of the earliest and most traditional approaches to software development. It’s characterized by its linear and sequential progression through different phases, with each phase being completed before the next one begins. This structured approach was inspired by traditional engineering and manufacturing processes, where each step had to be completed before moving forward.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the stages in the Waterfall model:
The Waterfall model is one of the earliest and most traditional approaches to software development. It’s characterized by its linear and sequential progression through different phases, with each phase being completed before the next one begins. This structured approach was inspired by traditional engineering and manufacturing processes, where each step had to be completed before moving forward.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the stages in the Waterfall model:
 The V-Model, also known as the Validation and Verification model, is an extension of the Waterfall model that emphasizes the relationship between development and testing. It is represented in a “V” shape, where the left side represents the development phases and the right side represents the corresponding testing phases. This model aims to ensure a strong alignment between development and testing activities, with the goal of delivering high-quality software.
Here’s a breakdown of the V-Model’s structure:
The V-Model, also known as the Validation and Verification model, is an extension of the Waterfall model that emphasizes the relationship between development and testing. It is represented in a “V” shape, where the left side represents the development phases and the right side represents the corresponding testing phases. This model aims to ensure a strong alignment between development and testing activities, with the goal of delivering high-quality software.
Here’s a breakdown of the V-Model’s structure:
 The Iterative and Incremental model is designed to address some of the limitations of the Waterfall model by introducing flexibility, adaptability, and the ability to accommodate changing requirements more effectively. It focuses on building the software through a series of small iterations, each of which adds incremental value to the overall product.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Iterative and Incremental model:
The Iterative and Incremental model is designed to address some of the limitations of the Waterfall model by introducing flexibility, adaptability, and the ability to accommodate changing requirements more effectively. It focuses on building the software through a series of small iterations, each of which adds incremental value to the overall product.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Iterative and Incremental model:
 The Prototyping model is a software development approach that focuses on creating prototypes or early versions of a software application to gather feedback, clarify requirements, and refine the final product before full development begins.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Prototyping model:
The Prototyping model is a software development approach that focuses on creating prototypes or early versions of a software application to gather feedback, clarify requirements, and refine the final product before full development begins.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Prototyping model:
 The Spiral Model is indeed a risk-driven software development model that emphasizes addressing risks and uncertainties throughout the project’s lifecycle. It is designed to be particularly suitable for projects where risk management is crucial due to the complexity of requirements, technology, or other factors.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Spiral Model:
The Spiral Model is indeed a risk-driven software development model that emphasizes addressing risks and uncertainties throughout the project’s lifecycle. It is designed to be particularly suitable for projects where risk management is crucial due to the complexity of requirements, technology, or other factors.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Spiral Model:
 The Scrum model is indeed one of the most popular Agile methodologies, emphasizing flexibility, collaboration, and iterative development. It uses short iterations called sprints to deliver incremental value to the project. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Scrum model:
The Scrum model is indeed one of the most popular Agile methodologies, emphasizing flexibility, collaboration, and iterative development. It uses short iterations called sprints to deliver incremental value to the project. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Scrum model:
 Kanban is indeed an Agile model that emphasizes continuous delivery and visual management. It’s particularly suitable for teams looking to optimize their workflow and manage work in progress more effectively. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Kanban model:
Kanban is indeed an Agile model that emphasizes continuous delivery and visual management. It’s particularly suitable for teams looking to optimize their workflow and manage work in progress more effectively. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Kanban model:
What are the Software Development Models?
Software development models, also known as methodologies, encompass a range of processes adopted for project development based on specific project objectives. These models outline distinct development life cycles, tailored to achieve various desired outcomes. By defining the stages of the process and their sequential execution, these models serve as blueprints for software creation. The choice of model should align with project objectives, team dynamics, customer requirements, and available resources. Each model offers a unique approach to software creation, emphasizing different aspects of the development process. Here are some of the most well-known software development models:- Waterfall model
- V model
- Iterative model
- Prototyping Model
- Spiral Model
- Scrum Model
- Kanban Model
Software Engineering Development Models
Certainly, let’s delve into seven of the most popular software development models in engineering. These models play a pivotal role in shaping a project’s quality, budget, timeline, and ultimately, stakeholder satisfaction.Waterfall Model
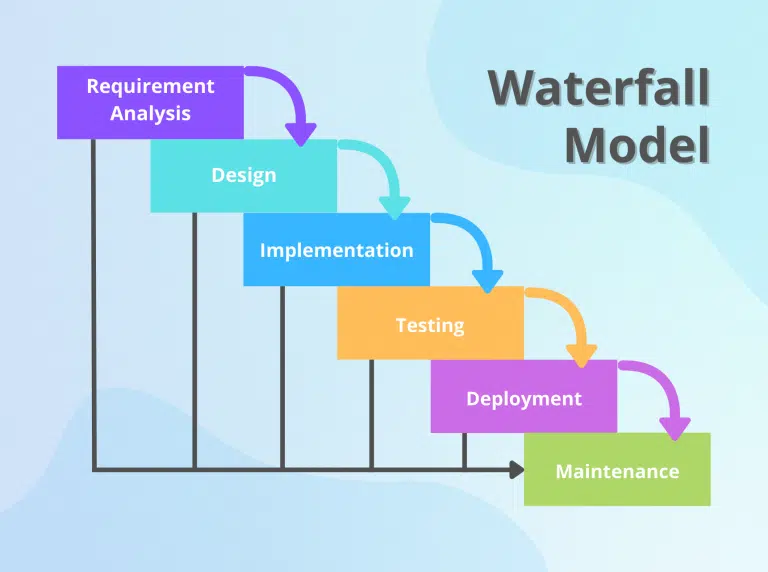 The Waterfall model is one of the earliest and most traditional approaches to software development. It’s characterized by its linear and sequential progression through different phases, with each phase being completed before the next one begins. This structured approach was inspired by traditional engineering and manufacturing processes, where each step had to be completed before moving forward.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the stages in the Waterfall model:
The Waterfall model is one of the earliest and most traditional approaches to software development. It’s characterized by its linear and sequential progression through different phases, with each phase being completed before the next one begins. This structured approach was inspired by traditional engineering and manufacturing processes, where each step had to be completed before moving forward.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the stages in the Waterfall model:
-
Requirements Gathering and Analysis:
-
System Design:
-
Implementation (Coding):
-
Testing:
-
Deployment:
-
Maintenance:
V-Model
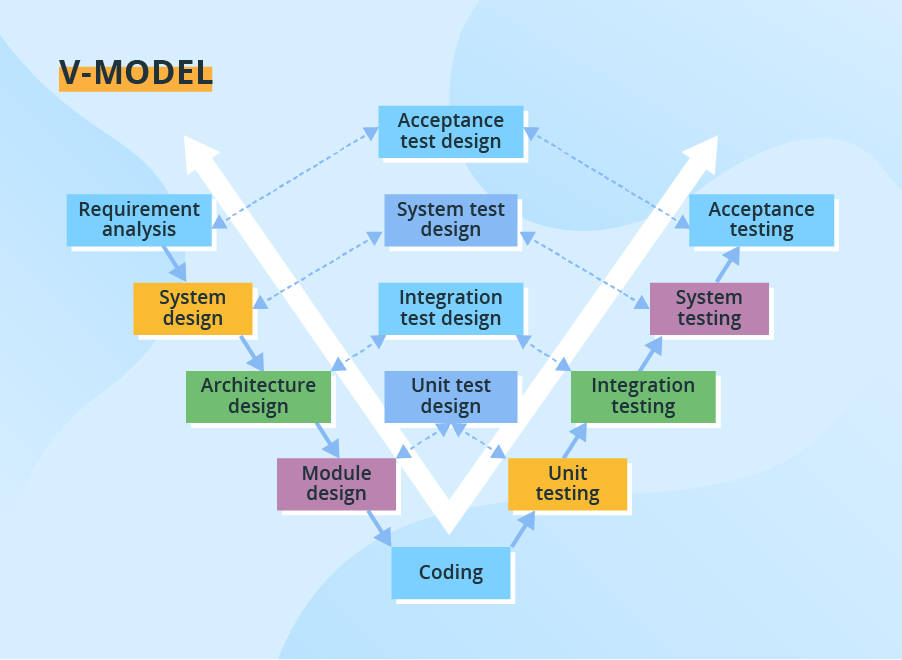 The V-Model, also known as the Validation and Verification model, is an extension of the Waterfall model that emphasizes the relationship between development and testing. It is represented in a “V” shape, where the left side represents the development phases and the right side represents the corresponding testing phases. This model aims to ensure a strong alignment between development and testing activities, with the goal of delivering high-quality software.
Here’s a breakdown of the V-Model’s structure:
The V-Model, also known as the Validation and Verification model, is an extension of the Waterfall model that emphasizes the relationship between development and testing. It is represented in a “V” shape, where the left side represents the development phases and the right side represents the corresponding testing phases. This model aims to ensure a strong alignment between development and testing activities, with the goal of delivering high-quality software.
Here’s a breakdown of the V-Model’s structure:
-
Requirements Phase:
-
System Design Phase:
-
Module/Component Design Phase:
-
Implementation (Coding) Phase:
-
Unit Testing:
-
Integration Testing:
-
System Testing:
-
Acceptance Testing:
-
Deployment:
Iterative (and Incremental) Model
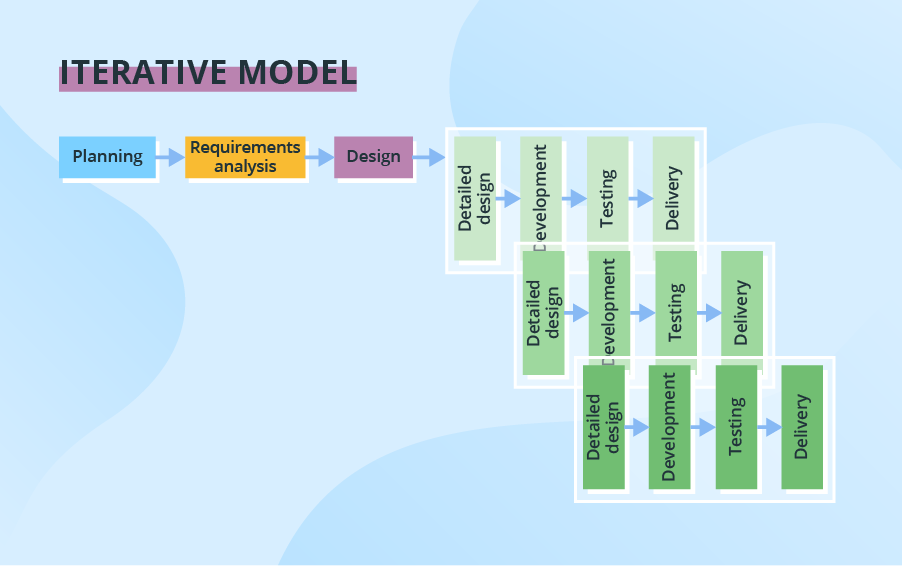 The Iterative and Incremental model is designed to address some of the limitations of the Waterfall model by introducing flexibility, adaptability, and the ability to accommodate changing requirements more effectively. It focuses on building the software through a series of small iterations, each of which adds incremental value to the overall product.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Iterative and Incremental model:
The Iterative and Incremental model is designed to address some of the limitations of the Waterfall model by introducing flexibility, adaptability, and the ability to accommodate changing requirements more effectively. It focuses on building the software through a series of small iterations, each of which adds incremental value to the overall product.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Iterative and Incremental model:
-
Requirements Gathering and Initial Planning:
-
Iteration 1:
-
Iteration 2:
-
Iteration N:
-
Final Deployment:
Prototyping Model
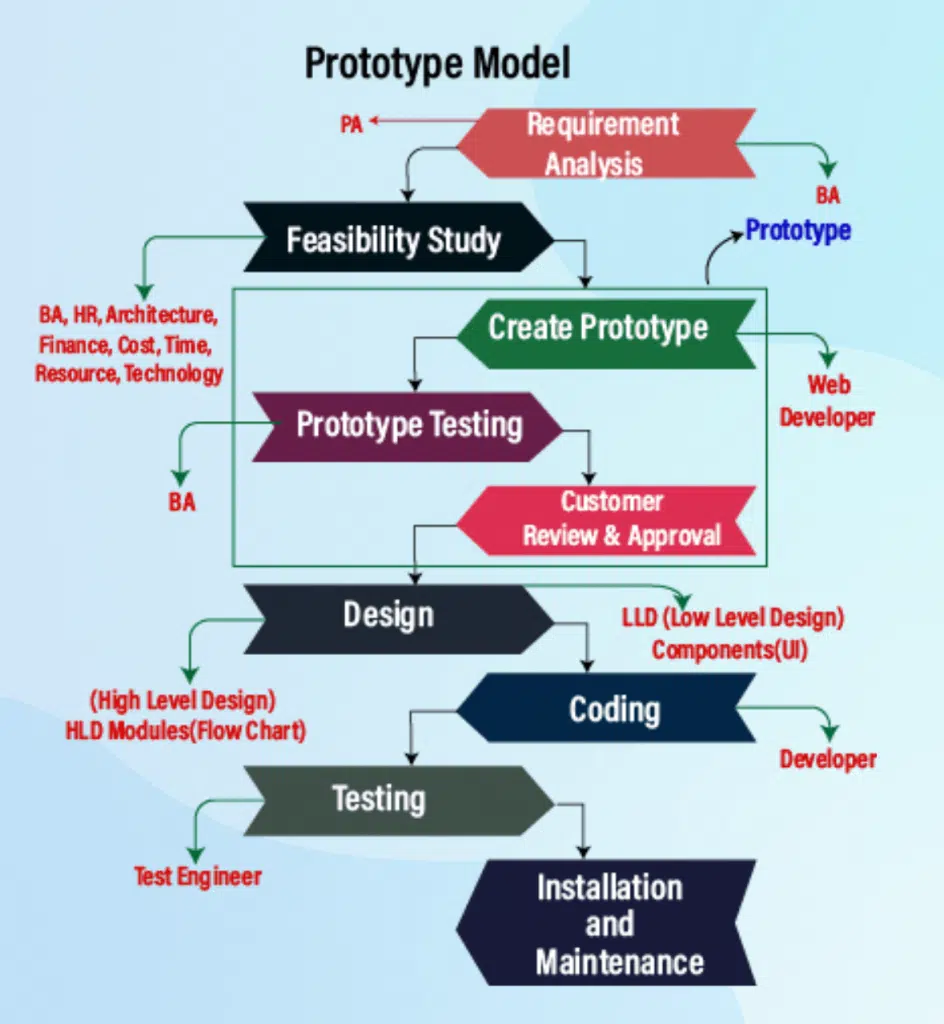 The Prototyping model is a software development approach that focuses on creating prototypes or early versions of a software application to gather feedback, clarify requirements, and refine the final product before full development begins.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Prototyping model:
The Prototyping model is a software development approach that focuses on creating prototypes or early versions of a software application to gather feedback, clarify requirements, and refine the final product before full development begins.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Prototyping model:
-
Requirements Gathering and Initial Understanding:
-
Prototyping Phase:
-
Feedback and Refinement:
-
Prototype Iterations:
-
Final Product Development:
Spiral Model
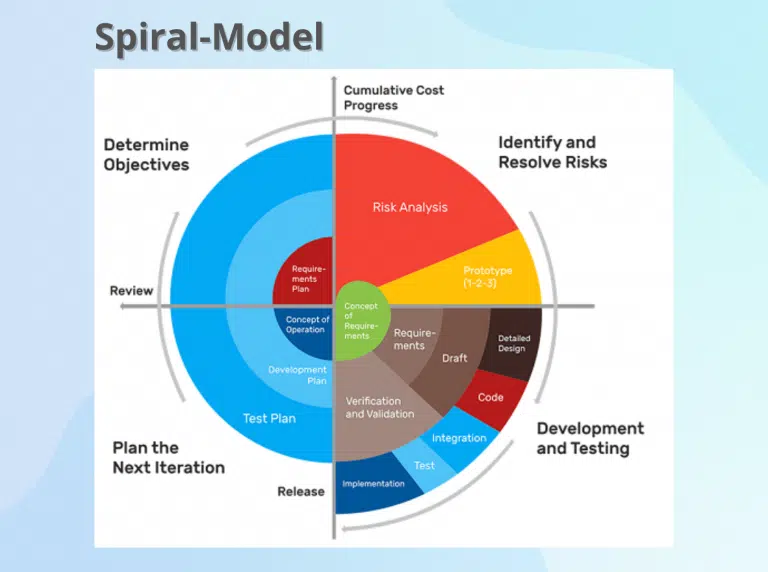 The Spiral Model is indeed a risk-driven software development model that emphasizes addressing risks and uncertainties throughout the project’s lifecycle. It is designed to be particularly suitable for projects where risk management is crucial due to the complexity of requirements, technology, or other factors.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Spiral Model:
The Spiral Model is indeed a risk-driven software development model that emphasizes addressing risks and uncertainties throughout the project’s lifecycle. It is designed to be particularly suitable for projects where risk management is crucial due to the complexity of requirements, technology, or other factors.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Spiral Model:
-
Planning:
-
Risk Analysis:
-
Engineering (Development and Prototyping):
-
Evaluation:
Scrum Model
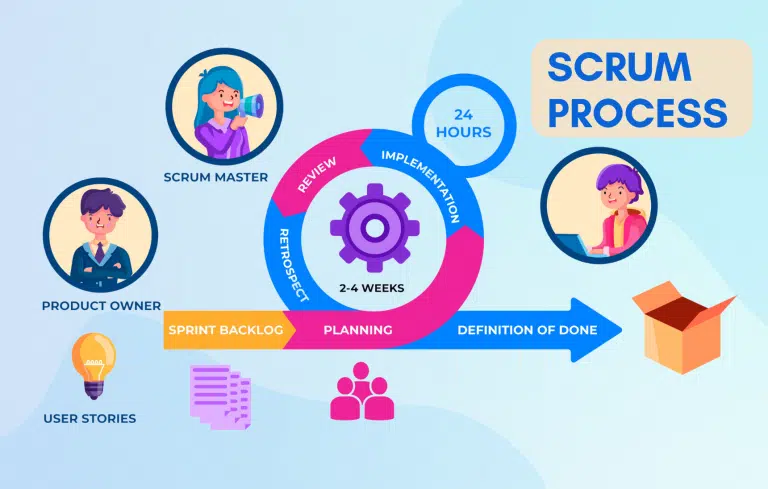 The Scrum model is indeed one of the most popular Agile methodologies, emphasizing flexibility, collaboration, and iterative development. It uses short iterations called sprints to deliver incremental value to the project. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Scrum model:
The Scrum model is indeed one of the most popular Agile methodologies, emphasizing flexibility, collaboration, and iterative development. It uses short iterations called sprints to deliver incremental value to the project. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Scrum model:
-
Sprints:
-
Sprint Planning:
-
Daily Stand-ups:
-
Sprint Review:
-
Sprint Retrospective:
-
Backlog Refinement:
-
Incremental Development:
-
Release Planning:
Kanban Model
 Kanban is indeed an Agile model that emphasizes continuous delivery and visual management. It’s particularly suitable for teams looking to optimize their workflow and manage work in progress more effectively. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Kanban model:
Kanban is indeed an Agile model that emphasizes continuous delivery and visual management. It’s particularly suitable for teams looking to optimize their workflow and manage work in progress more effectively. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the Kanban model:
-
Continuous Flow:
-
Visual Management:
-
Work in Progress (WIP) Limits:
-
Short Iterations (Optional):
-
Continuous Improvement:
-
Flexibility and Customer Focus:
-
Feature Concentration: